Blog
- Home
- Blog
How to Choose the Right Valve Steel for Your Industrial Applications
Selecting the appropriate valve steel for industrial applications is a critical decision that can significantly influence operational efficiency and safety. As the demand for high-performance valves continues to rise across industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing, understanding the specific properties and applications of various valve steel grades becomes increasingly essential. According to a recent report by the Global Valve Market Analysis, the valve steel market is expected to grow by 5% annually through 2025, driven by advancements in manufacturing techniques and an increasing focus on durability and corrosion resistance.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Thornton, a metallurgist with over 15 years of experience in valve manufacturing, emphasizes, "The choice of valve steel is not just about meeting basic specifications; it is about defining performance and longevity in demanding environments." This sentiment highlights the importance of considering factors such as temperature resistance, tensile strength, and ductility when selecting valve steel. As industrial applications evolve, so too must the materials chosen to withstand the rigors of a complex operating landscape. Therefore, making an informed decision regarding valve steel selection is vital for achieving optimal performance and minimizing costly downtime.

Understanding the Importance of Valve Steel Selection in Industry
Selecting the appropriate valve steel is a critical aspect in various industrial applications, as it directly influences the performance and longevity of equipment. According to a report by the International Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, approximately 30% of industrial failures can be attributed to inadequate material selection, which highlights the heavy toll that poor valve steel choices can take on productivity and safety. In industries such as oil and gas, where conditions can be extreme, it is essential to understand that materials must withstand not only high pressures but also corrosive environments.
The selection process involves assessing various factors, including mechanical properties, temperature tolerance, and corrosion resistance. For instance, data from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers indicates that valve steels must exhibit yield strength of at least 200 ksi for high-pressure applications to ensure durability. In sectors such as chemical processing, where exposure to aggressive substances is routine, the choice of stainless steel or alloy steels with specific compositions can prevent catastrophic failures. Hence, proper valve steel selection not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates the risk of costly downtime due to equipment malfunction, making it an indispensable consideration for industrial operations.
How to Choose the Right Valve Steel for Your Industrial Applications
| Steel Type | Hardness (HB) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Corrosion Resistance | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 304 | 152 | 520 | 215 | Good | Food Processing, Chemical Equipment |
| AISI 316 | 152 | 580 | 250 | Excellent | Marine Applications, Pharmaceutical Equipment |
| AISI 420 | 325 | 750 | 360 | Moderate | Knife Blades, Valve Components |
| AISI 1045 | 198 | 620 | 350 | Poor | Machinery Components, Shafting |
Key Properties of Valve Steels: Strength, Toughness, and Corrosion Resistance
Choosing the right valve steel is crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance of industrial applications. When evaluating valve steels, three key properties come to the forefront: strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance. Strength is essential to withstand internal pressure and stress during operation. High tensile strength materials are often preferred in applications that see extreme conditions. For instance, according to a recent industry report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), steels with a tensile strength of over 800 MPa have shown improved performance in high-pressure environments, reducing the likelihood of valve failure.
Toughness is another vital property, particularly in applications where valves undergo significant thermal and mechanical fatigue. Tough steels can absorb energy from impacts without fracturing, making them ideal for environments with fluctuating temperatures. A study published in the Journal of Materials Science highlights that steels with Charpy impact values above 30 Joules at sub-zero temperatures offer enhanced durability in cryogenic applications, ensuring continuous operation even under severe conditions.
Corrosion resistance cannot be overlooked, especially in industries dealing with harsh chemicals or saline environments. Selecting valve steels with high chromium content or using surface treatments can substantially improve their resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. Industry data indicates that stainless steels like 316L can achieve up to 12 times better corrosion resistance compared to standard carbon steels in maritime applications.
Tips: When choosing valve steel, always consider the specific operating environment and application requirements. Consult with materials engineers to evaluate steel grades and treatments that align with your operational demands. Regular inspections and maintenance can also enhance the longevity of the components, minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
Key Properties of Valve Steels
This bar chart illustrates the key properties of valve steels. It showcases the ideal ranges for strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, which are critical factors to consider when selecting valve steels for industrial applications.
Comparing Common Valve Steel Grades: ASTM A276 vs. Aisi 4130
When selecting the appropriate valve steel for industrial applications, it is crucial to compare the characteristics of common steel grades such as ASTM A276 and AISI 4130. The A276 specification covers stainless steels with a variety of corrosion resistance properties, making it suitable for harsh environments where rust and corrosion can compromise the integrity of valve components. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), ASTM A276 steel is often used for valves in chemical processing facilities and power generation, where its strength and corrosion resistance ensure reliability and longevity in operation.
On the other hand, AISI 4130 is a low-alloy steel that is known for its high strength, toughness, and weldability, making it a popular choice for the oil and gas industry as well as aerospace applications. This steel grade typically has a higher tensile strength and yield strength compared to stainless grades such as ASTM A276, with values often exceeding 70,000 psi in ultimate tensile strength testing (according to industry data). When valves are required to withstand high pressures and extreme operating conditions, AISI 4130's mechanical properties come into play, making it an ideal candidate for high-stress applications.
Ultimately, the choice between ASTM A276 and AISI 4130 will depend heavily on the specific requirements of the application, such as environmental conditions, pressure levels, and the necessary corrosion resistance. Evaluating these factors allows engineers to make informed decisions that can significantly impact the efficiency and safety of their operations.
Impact of Temperature and Pressure on Valve Steel Performance
When selecting valve steel for industrial applications, understanding the impact of temperature and pressure on performance is crucial. High temperatures can lead to thermal expansion and reduce a steel's yield strength, making it susceptible to deformation. Specifically, as temperatures rise, the mechanical properties of steel can change significantly. A steel that performs well at ambient temperatures may lose its integrity at elevated temperatures, potentially leading to catastrophic failures in high-temperature environments. Thus, it's essential to choose materials with high-temperature stability and resistance to oxidation for applications that operate under such conditions.
Pressure, on the other hand, plays a role in the overall stress experienced by valve components. Higher pressure levels can exacerbate material fatigue and increase the risk of cracking, especially in steels that have not been specifically engineered to withstand these conditions. It's vital to consider the combination of both temperature and pressure when selecting valve steel, as they often interact. Material selection should prioritize alloys that have demonstrated durability and resistance under both high-pressure and high-temperature scenarios. This approach ensures that the valve will maintain its functionality and safety in demanding industrial environments, prolonging service life and reducing the risk of unexpected downtime.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Different Valve Steel Options for Applications
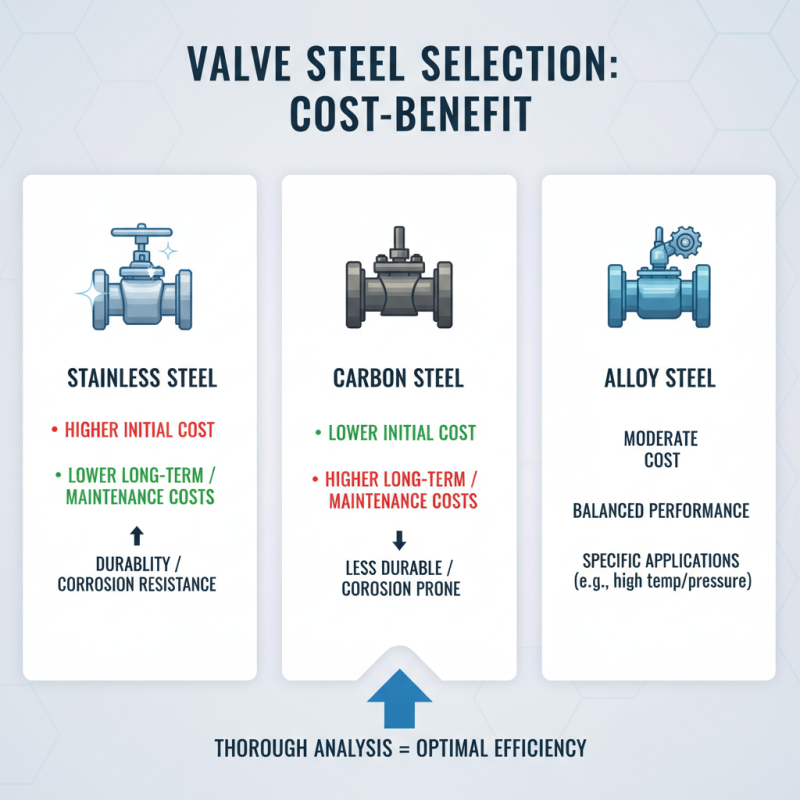
When selecting the appropriate valve steel for industrial applications, a thorough cost-benefit analysis is essential for determining the most viable options. Various types of valve steel, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel, present different initial costs and long-term benefits that can significantly impact operational efficiency. Stainless steel, for example, may have a higher upfront cost due to its corrosion-resistant properties, but its durability can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs over time. In contrast, carbon steel might be more affordable initially, but it may require more frequent repairs and replacements in harsh environments, which could offset the initial savings.
Additionally, the choice of valve steel should also consider the specific operational requirements and environmental conditions of the application. For instance, industries dealing with high temperatures and pressures often benefit from high-performance alloy steels, despite their increased cost. Conducting a comprehensive analysis that weighs factors such as performance lifespan, maintenance needs, and environmental resistance against the purchase price enables companies to make informed decisions that align with their budget and operational goals. Ultimately, the right valve steel can enhance productivity and reduce long-term expenses, proving that an upfront investment can yield significant returns in an industrial setting.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Valve Steel for Your Projects
-

Top Benefits of Engineered Valves for Industrial Applications
-

10 Best Valve Applications for Efficient Industrial Processes
-
Understanding the Role of Guide Valves in Modern Hydraulic Systems
-

Discover the Best DHV Gate Valve Options for 2025 Top Digital Applications
-

What is Steel Valves and How They Benefit Your Industrial Applications
 (780) 669-9420
(780) 669-9420
